Objectives of the Hierarchical Taxonomy of Psychopathology (HiTOP) are to advance the classification of psychopathology to maximize its usefulness for research and clinical practice. The HiTOP aims to address limitations of traditional nosologies, such as the DSM-5 and ICD-10, including arbitrary boundaries between psychopathology and normality, often unclear boundaries between disorders, frequent disorder co-occurrence, heterogeneity within disorders, and diagnostic instability.
The HiTOP approaches these problems by conducting an empirical search for psychopathology structures starting from the most basic building blocks and proceeding to the highest level of generality: combining individual signs and symptoms into homogeneous components or traits, assembling them into empirically-derived syndromes, and finally grouping them into psychopathology spectra (e.g., internalizing and externalizing).
This approach reduces within-disorder heterogeneity by grouping related symptoms together and assigning unrelated symptoms to different components. It makes comorbidity an explicit and predictable feature of the model by classifying related syndromes together. Finally, it describes psychiatric phenomena dimensionally, addressing boundary problems and diagnostic instability. The HiTOP is not limited to dimensions, if evidence indicates existence of a natural boundary, this qualitative distinction will be incorporated in the model also.
The HiTOP system aims to significantly advance mental health research and care, providing an effective way to convey information on risk factors, etiology, pathophysiology, phenomenology, illness course, and treatment response, thus greatly improving the utility of the diagnosis of mental disorders. Dimensional measures have been developed to assess many aspects of the system, and several domains of the HiTOP are ready for clinical and research applications.
The HiTOP Consortium values diversity and is committed to the recruitment and inclusion of members from diverse and underrepresented backgrounds. We believe that a diverse membership, including individuals with different lived experiences and identities (e.g., those defined by gender, race/ethnic, nationality, sexual orientation, socioeconomic status, disability), is critical to achieving our aims of understanding the experience of psychopathology as a shared human condition. Along these lines, it is our goal to provide a framework of professional support for individuals from diverse backgrounds across career stages. Finally, we believe that advancements in mental disorder classification can be applied to understanding, preventing, and ameliorating mental health disparities across populations and identifying the causes and effects of such disparities. Accordingly, we are committed to testing the structure of psychopathology directly in diverse samples.
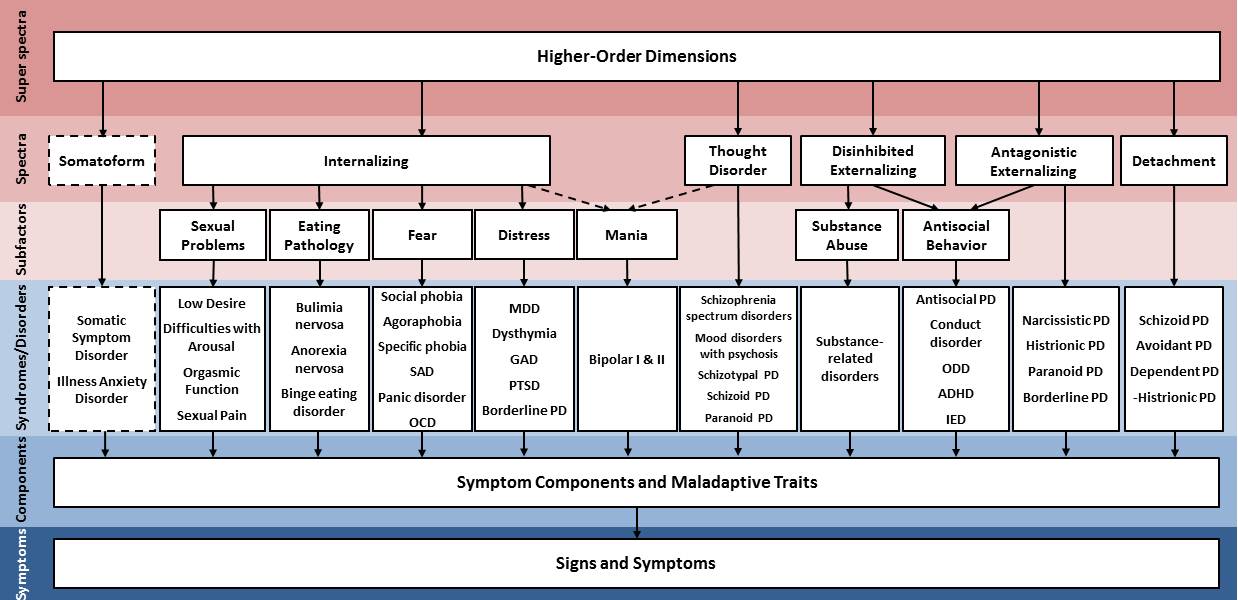
The system is a work in progress. Figure below summarizes how eleven DSM-5 classes of mental disorders have been incorporated into the HiTOP to date.