More than 30 million Americans suffer from a thyroid disorder, and many more go undiagnosed every year. Now is a good time to become aware of your thyroid and its relationship to your health — and how best to take care of it.
Thyroid nodules and enlarged thyroid glands are common problems, and they can harbor cancers within them. They require proper evaluation and treatment.
When detected, patients with these thyroid disorders are usually referred for further work-up to an endocrinologist, or to an experienced head and neck surgeon, like one of the head and neck surgeons at Stony Brook Medicine.
January is national Thyroid Awareness Month that aims to bring to the public's attention the need to take good care of this important tiny gland in the neck.
Following a thorough work-up, the patient may need to undergo thyroidectomy (removal of part or all of the thyroid gland) for several reasons — for removal of thyroid cancer, removal of part of the thyroid gland for definitive diagnosis, treatment of a hyperactive thyroid gland, or an enlarged thyroid gland that is causing breathing or swallowing difficulties.
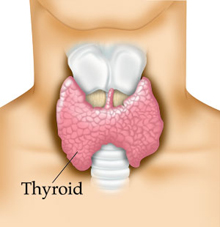
The thyroid gland is a small, butterfly-shaped gland located in the base of the neck just below the Adam's apple. Although relatively small, the thyroid gland influences the function of many of the body’s most important organs, including the heart, brain, liver, kidneys, and skin. Ensuring that the thyroid gland is healthy and functioning properly is important to the body's overall well-being.
Surgical intervention is the gold standard in thyroid cancer; there are no other options to cure it.
Since thyroid cancers are highly curable, it is extremely important for the patient to undergo proper treatment and close follow-up. The initial treatment for most thyroid cancers is removal of the thyroid gland, and sometimes removal of lymph nodes which may contain metastatic cancer.
In the hands of a highly-skilled, experienced surgeon, the procedure can usually be done on an outpatient basis and with a low risk of complications. Depending on the type of cancer, some patients may require treatment with radioactive iodine after surgery.

| Our thyroid specialists, (l to r) Drs. Lukasz Czerwonka, Melissa M. Mortensen, Elliot Regenbogen, and Ghassan J. Samara. |
Also essential is close follow-up by the patient's endocrinologist for tumor surveillance and regulation of the thyroid hormone.
Our thyroid specialists take a multidisciplinary approach to providing care for patients with thyroid disorders. The team of physicians consists of surgeons, endocrinologists, radiation oncologists, radiologists, and pathologists.
Management decisions are often made jointly among the team members. Such a team approach has ensured long-term successful outcomes for our patients at Stony Brook Medicine.
Hyperthyroidism is a sustained overly active thyroid gland, which may result in anxiety, nervousness, rapid heartbeat, weight loss, and high blood pressure. The causes of hyperthyroidism include Grave's disease and toxic nodular goiter. This condition is treated with medications, radioactive iodine, or thyroidectomy.
The advantage of surgery is that the condition can be treated quickly and effectively, minimizing the risk of recurrence. In the past, non-surgical treatment has been the primary approach to patient care because of potential complications associated with the surgery. Now, with surgical expertise and advances in technology at Stony Brook Medicine, more patients are undergoing surgery with minimal complications.
In the past, goiter was treated with medication, but that was proved not to be effective. Patients with goiter now have surgery to alleviate the pressure symptoms on the trachea and the esophagus.
Thyroidectomy is performed for nodules and cancer of the thyroid gland. It is also performed in some patients with overactive thyroid glands.
Stony Brook Medicine provides patients state-of-the-art thyroid care using the multidisciplinary team approach, distinguished by highly experienced surgical specialists capable of treating all forms of thyroid conditions.
| The thyroid gland is a small, butterfly-shaped gland located in the base of the neck just below the Adam's apple. Although relatively small, the thyroid gland influences the function of many of the body’s most important organs, including the heart, brain, liver, kidneys, and skin. The blue paisley ribbon icon is the universal symbol of thyroid disease awareness and advocacy. Paisley was chosen because it resembles a cross-section of thyroid follicles, the tiny spheres that the thyroid gland is made of. |
Perform the do-it-yourself thyroid neck check. Watch this video (1:00 min) about thyroid awareness from the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists: